Currently Empty: ₹0.00
Child Development
Shaping Future Generations with Pedagogy Perspectives
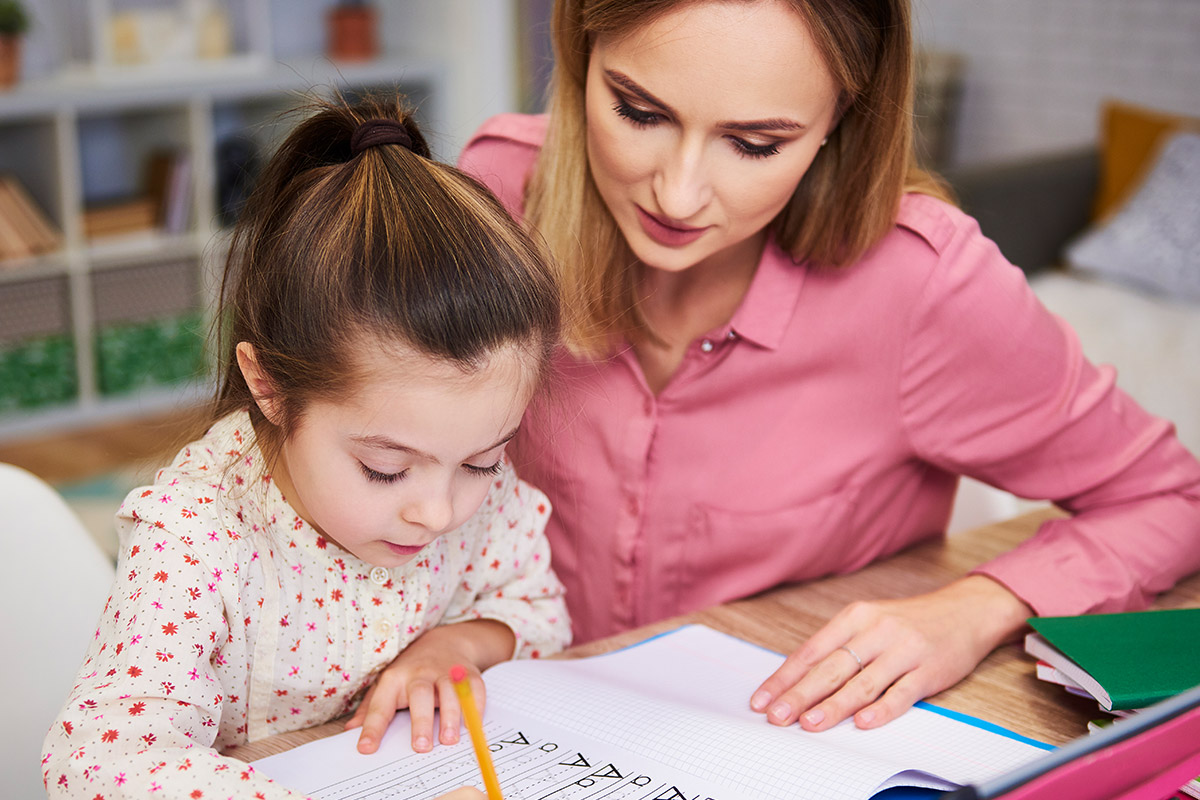

Shaping Future Generations with Pedagogy Perspectives
Pedagogy, the art and science of teaching, plays a critical role in shaping the future of students, guiding them not only in academic pursuits but also in personal growth and social development. With the evolving nature of education in today’s world, the importance of a thoughtful and adaptable approach to teaching has never been more pronounced. This blog delves into the key perspectives on pedagogy that are instrumental in shaping future generations and highlights how educators can harness these perspectives to foster holistic development.
1. Understanding Pedagogy: The Foundation of Teaching
Pedagogy is more than just delivering content—it’s the holistic practice of guiding students through their educational journey. It encompasses methods, strategies, philosophies, and approaches used to impart knowledge and foster intellectual, emotional, and social growth.
1.1 The Importance of Pedagogical Philosophy
Every educator, whether consciously or unconsciously, operates from a pedagogical philosophy. This philosophy influences how they view the learning process, the role of the teacher, and the responsibilities of the student. Common pedagogical philosophies include:
- Teacher-Centered Approach: The traditional model where the teacher is the primary source of knowledge, delivering content to students who passively receive it.
- Student-Centered Approach: This model emphasizes active participation by students, encouraging them to construct their own understanding and knowledge through experience and inquiry.
- Constructivist Approach: Rooted in the belief that learners build new knowledge by integrating new experiences with existing understanding, constructivist pedagogy stresses the importance of critical thinking and problem-solving.
These foundational philosophies shape the way educators engage with students, plan lessons, and assess outcomes.
2. The Role of Pedagogy in Student Development
Pedagogy directly influences the academic, emotional, and social growth of students. When implemented thoughtfully, it encourages learners to develop critical thinking, creativity, empathy, and a lifelong love of learning.
2.1 Academic Growth
Pedagogy lays the groundwork for academic success by influencing the way content is delivered and absorbed. By incorporating a mix of teaching styles, educators can cater to diverse learning preferences, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners.
- Differentiated Instruction: Tailoring lessons to meet the needs of individual students or groups ensures that all learners, regardless of their abilities, can access the material.
- Scaffolding: This instructional method involves breaking down learning into smaller, more manageable steps, providing support at each stage to help students build a solid understanding of complex concepts.
By adjusting their pedagogy to the needs of their students, educators can help foster deeper comprehension, retention, and application of knowledge.
2.2 Emotional and Social Growth
Beyond academics, pedagogy plays a significant role in emotional and social development. Classrooms are microcosms of society, and the pedagogical practices employed can shape how students interact with others, handle conflicts, and develop empathy.
- Social-Emotional Learning (SEL): This approach integrates emotional intelligence, self-awareness, and interpersonal skills into the learning process. Through SEL, students learn to manage emotions, set goals, show empathy, and maintain positive relationships.
- Collaborative Learning: Group activities and peer-to-peer learning foster teamwork, communication, and leadership skills. This form of pedagogy encourages students to learn from each other and promotes a culture of respect and collaboration.
Educators who recognize the importance of emotional and social growth alongside academic success help shape well-rounded, emotionally intelligent individuals who are prepared to contribute positively to society.
3. Key Pedagogical Perspectives
Pedagogy has evolved significantly over the years, and various perspectives have emerged that cater to different educational goals. Below are some of the key perspectives that influence modern teaching practices:
3.1 Behaviorism
Behaviorist pedagogy focuses on observable behaviors and how they can be shaped through reinforcement and punishment. This perspective is based on the idea that learning occurs through interaction with the environment.
- Positive Reinforcement: Rewards are given to encourage desired behaviors, such as completing homework on time or answering questions correctly.
- Negative Reinforcement: Unwanted behaviors are discouraged through consequences, like loss of privileges or extra assignments.
While behaviorism has limitations, especially in terms of promoting deeper critical thinking, it is effective for instilling discipline and foundational knowledge.
3.2 Constructivism
Constructivism is a student-centered approach that believes learners build their understanding of the world through experiences and reflection.
- Active Learning: Students are encouraged to explore, question, and problem-solve, leading to deeper understanding and retention of knowledge.
- Project-Based Learning (PBL): This hands-on method allows students to work on real-world projects, which fosters engagement and allows them to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations.
Constructivist pedagogy encourages critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving, making it ideal for modern classrooms where students are expected to be more autonomous and self-directed learners.
3.3 Experiential Learning
Experiential learning focuses on learning through experience, often referred to as “learning by doing.”
- Hands-On Activities: Whether it’s science experiments, art projects, or field trips, this pedagogy emphasizes that students learn best when they are actively engaged in the learning process.
- Reflection: After an experience, students are encouraged to reflect on what they’ve learned and how it applies to broader concepts or real-life situations.
Experiential learning is particularly valuable for developing practical skills and understanding complex concepts in a concrete, hands-on way.
3.4 Critical Pedagogy
Critical pedagogy, rooted in the works of educators like Paulo Freire, encourages students to question power structures and societal norms. It’s a transformative approach that aims to empower students to challenge injustice and inequality.
- Empowerment through Education: Critical pedagogy teaches students to think critically about the world around them and to see education as a tool for social change.
- Culturally Responsive Teaching: This approach embraces the diverse cultural backgrounds of students, integrating their experiences and perspectives into the curriculum to foster inclusivity and equity.
Critical pedagogy is especially relevant in today’s diverse classrooms, where students need to be prepared to navigate and contribute to a complex, interconnected world.
4. Incorporating Technology into Pedagogy
In the 21st century, technology plays a vital role in modern pedagogy. Integrating digital tools into teaching not only enhances learning but also prepares students for the digital age.
4.1 Blended Learning
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online learning. This approach allows for greater flexibility and personalization.
- Flipped Classroom: In this model, students access lectures and content at home via digital platforms and engage in collaborative activities in the classroom.
- Online Assessments and Feedback: Digital tools allow for instant feedback, helping students to quickly identify areas for improvement and allowing teachers to track progress more efficiently.
Blended learning provides a dynamic, interactive environment that caters to the diverse needs of students, enhancing engagement and motivation.
4.2 Gamification and Interactive Tools
Gamification uses elements of game design, such as points, rewards, and competition, to make learning more engaging.
- Educational Apps and Games: Tools like Kahoot!, Quizlet, and Duolingo make learning fun and interactive, while also reinforcing concepts in an engaging way.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These technologies offer immersive learning experiences, allowing students to explore historical events, scientific phenomena, and more in a hands-on, interactive way.
Integrating technology into pedagogy not only makes learning more accessible but also prepares students for a future where digital literacy is essential.
5. Pedagogical Challenges and Opportunities
While pedagogy offers a range of opportunities for shaping future generations, educators also face significant challenges in implementing effective teaching strategies.
5.1 Addressing Diverse Learning Needs
In any classroom, students come with diverse abilities, learning styles, and backgrounds. Creating an inclusive learning environment that caters to all students is one of the biggest challenges for educators today.
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): This framework provides multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression, ensuring that all students, including those with disabilities, can access the curriculum.
- Culturally Responsive Teaching: Embracing the cultural backgrounds of students and incorporating their experiences into the learning process helps create an inclusive environment that respects diversity.
5.2 Time Constraints and Curriculum Demands
Teachers are often constrained by strict curriculums and limited time, making it difficult to implement student-centered, inquiry-based approaches.
- Balancing Content and Creativity: While meeting curriculum standards is important, educators should strive to integrate creative, critical thinking activities that allow students to explore beyond the textbook.
- Professional Development: Ongoing training and support for teachers are essential in helping them manage the demands of modern pedagogy while keeping up with new teaching techniques and technologies.
Conclusion: The Future of Pedagogy
Pedagogy is ever-evolving, and as educators look to the future, it is essential to adopt teaching practices that not only impart knowledge but also foster critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence. The perspectives on pedagogy outlined in this blog—from constructivism and critical pedagogy to the integration of technology—are key to shaping future generations.
Educators who embrace these pedagogical strategies will help cultivate students who are not only academically proficient but also socially responsible, emotionally intelligent, and equipped to navigate the complexities of the modern world. As education continues to evolve, so too must pedagogy, adapting to meet the needs of diverse learners and preparing them for a rapidly changing future.