Currently Empty: ₹0.00
Nutrition
Discover the Power of Nutrient-Rich Foods
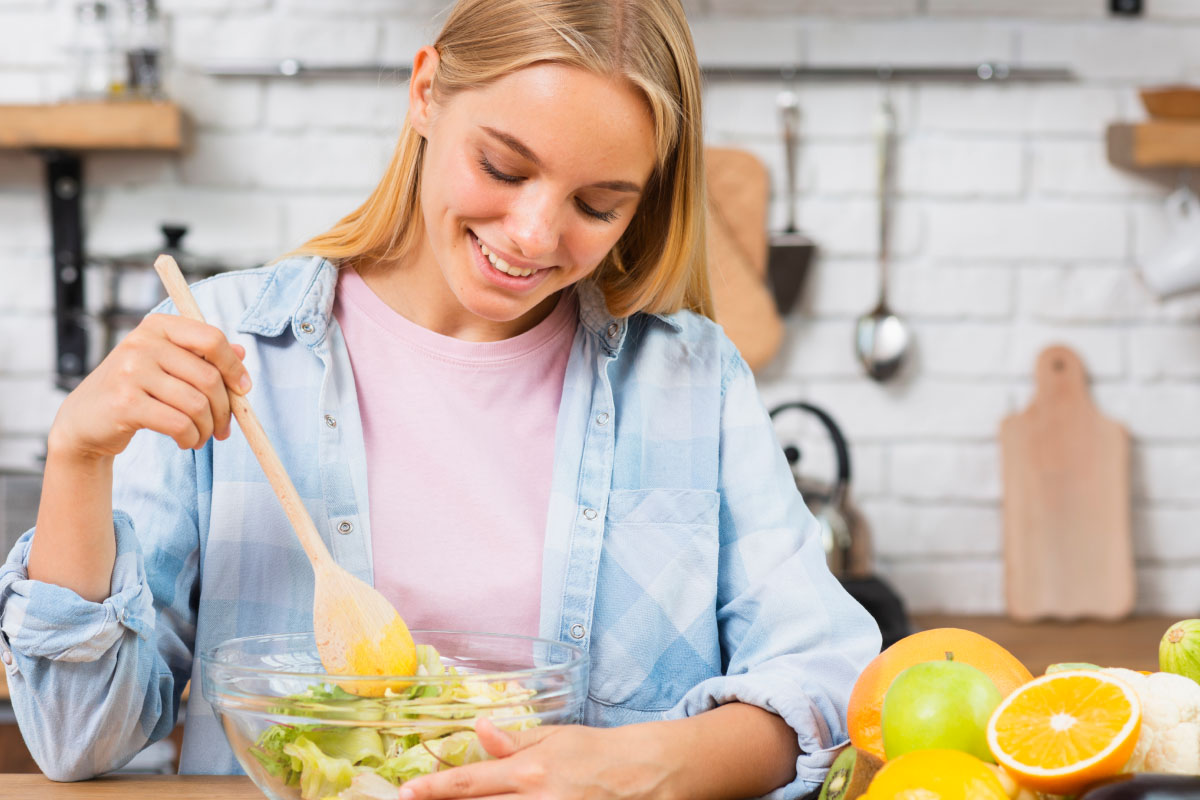

Discover the Power of Nutrient-Rich Foods: Fuel Your Body for Health and Vitality
Introduction: The Foundation of a Healthy Diet
In a world where processed foods and fast meals dominate our choices, it’s easy to overlook the importance of nutrient-dense foods. Nutrient-rich foods—those packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and essential nutrients—are key to maintaining energy, promoting wellness, and preventing chronic diseases. This blog will guide you through the benefits of nutrient-rich foods and offer tips on how to incorporate them into your daily routine.
1. What Are Nutrient-Rich Foods?
Nutrient-rich foods, also called nutrient-dense foods, are foods that provide a high level of nutrients relative to their calorie content. This means they are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, healthy fats, and protein, but relatively low in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excess calories. The goal is to get the most nutrition out of every bite.
Examples of Nutrient-Rich Foods:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, Swiss chard
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseeds, chia seeds
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, oats, brown rice
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, sardines, mackerel
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans
2. The Benefits of Eating Nutrient-Dense Foods
2.1 Boosts Energy Levels
Nutrient-rich foods provide sustained energy throughout the day. Unlike processed foods that give you a quick sugar rush followed by a crash, whole foods release energy slowly, keeping you fueled for longer.
For example, whole grains like oats contain complex carbohydrates that break down slowly, providing a steady supply of glucose for energy.
2.2 Supports Immune Function
Nutrient-rich foods are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that strengthen your immune system. Vitamin C in oranges, bell peppers, and strawberries plays a crucial role in immune health by supporting the production of white blood cells, which fight infections.
2.3 Promotes Weight Management
Because nutrient-dense foods are high in fiber and water content, they help you feel full and satisfied without over-consuming calories. Leafy greens, for instance, are low in calories but high in volume, making them ideal for weight management.
2.4 Reduces the Risk of Chronic Diseases
A diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon help lower inflammation and reduce the risk of heart disease, while fiber-rich foods like legumes help maintain healthy blood sugar levels and support gut health.
2.5 Enhances Skin and Hair Health
The vitamins and minerals in nutrient-rich foods also contribute to radiant skin and healthy hair. Vitamin A, found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach, helps maintain skin health by promoting cell turnover and reducing signs of aging.
3. Top 10 Nutrient-Rich Foods You Should Add to Your Diet
3.1 Spinach
Spinach is one of the most nutrient-dense leafy greens, rich in iron, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin K. It’s also packed with antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, which protect your eyes from damage caused by UV light and blue light from screens.
How to incorporate it:
- Add fresh spinach to your morning smoothie.
- Use spinach as a base for salads or sauté it as a side dish.
3.2 Blueberries
These small berries are antioxidant powerhouses, containing high levels of vitamin C, vitamin K, and fiber. Blueberries are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can help protect the brain from aging and cognitive decline.
How to incorporate it:
- Toss blueberries on top of yogurt, oatmeal, or cereal.
- Snack on fresh or frozen blueberries as a healthy dessert.
3.3 Salmon
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, salmon is an excellent source of protein and heart-healthy fats. Omega-3s play a role in reducing inflammation, supporting brain function, and improving cardiovascular health.
How to incorporate it:
- Grill or bake salmon for a nutritious dinner.
- Add smoked salmon to salads or whole grain toast with avocado.
3.4 Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. It’s also high in fiber, magnesium, and iron, making it a versatile and nutrient-packed grain alternative.
How to incorporate it:
- Substitute quinoa for rice in stir-fries and salads.
- Use quinoa as a base for grain bowls with vegetables and protein.
3.5 Almonds
Almonds are packed with vitamin E, magnesium, and healthy monounsaturated fats, which support heart health and reduce bad cholesterol levels. They’re also a great snack that promotes satiety.
How to incorporate it:
- Snack on a handful of almonds or add them to trail mix.
- Use almond butter as a spread or in smoothies for added creaminess.
3.6 Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene, which the body converts to vitamin A—essential for vision, immune function, and skin health. They are also high in fiber, promoting digestive health.
How to incorporate it:
- Roast sweet potatoes as a side dish or use them in soups.
- Mash sweet potatoes as a nutrient-dense alternative to regular mashed potatoes.
3.7 Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are a good source of fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and protein. They help with digestion, support heart health, and keep you feeling full longer.
How to incorporate it:
- Mix chia seeds into smoothies, yogurt, or overnight oats.
- Make a chia seed pudding by soaking them in almond milk with a natural sweetener.
3.8 Broccoli
Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable loaded with fiber, vitamins C and K, and folate. It contains sulforaphane, a compound that may have cancer-fighting properties.
How to incorporate it:
- Steam or roast broccoli as a side dish or mix it into casseroles.
- Add chopped broccoli to stir-fries or pasta dishes.
3.9 Lentils
Lentils are a great plant-based source of protein and fiber, making them a staple in vegetarian diets. They’re also rich in iron, folate, and potassium, supporting heart health and energy production.
How to incorporate it:
- Use lentils in soups, stews, or as a base for salads.
- Make a lentil-based veggie burger for a protein-packed meal.
3.10 Greek Yogurt
Greek yogurt is rich in protein, calcium, and probiotics, which support gut health. The probiotics in yogurt help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, essential for digestion and immune function.
How to incorporate it:
- Enjoy Greek yogurt with fresh fruit and honey as a breakfast or snack.
- Use Greek yogurt as a base for smoothies or in place of sour cream in dips.
4. Tips to Incorporate Nutrient-Rich Foods into Your Daily Diet
4.1 Plan Your Meals Ahead
Meal planning is key to ensuring you consume a balanced and nutrient-dense diet. Plan your meals and snacks for the week, focusing on including a variety of whole foods.
4.2 Prioritize Whole Foods Over Processed Foods
While processed foods are convenient, they are often stripped of nutrients and loaded with sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. Opt for whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
4.3 Experiment with Different Cooking Methods
Steaming, roasting, grilling, and sautéing are excellent ways to prepare nutrient-rich foods without adding excess calories or fat. For example, roasting vegetables brings out their natural sweetness and preserves their nutrients.
4.4 Add Color to Your Plate
The more colorful your plate, the more nutrient-dense it is likely to be. Different colored fruits and vegetables contain unique sets of vitamins and antioxidants. Aim for a “rainbow” of colors in every meal.
4.5 Snack Smart
Instead of reaching for chips or sugary snacks, opt for nutrient-rich snacks like a handful of nuts, fresh fruit, or hummus with carrot sticks.
5. The Importance of Hydration
While eating nutrient-rich foods is essential, staying hydrated is equally important. Water helps transport nutrients throughout the body, aids digestion, and keeps your skin hydrated. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and consider adding slices of fruit or herbs like mint for flavor.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Nutrient-Dense Foods
By prioritizing nutrient-rich foods, you’ll not only improve your overall health but also enjoy more energy, better digestion, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases. Start small by incorporating one or two nutrient-packed foods into your meals each day, and watch as your body responds to this positive change. Remember, food is fuel—make sure you’re fueling your body with the best!