Currently Empty: ₹0.00
Nutrition
Fueling Your Body for Success: A Nutrition Guide
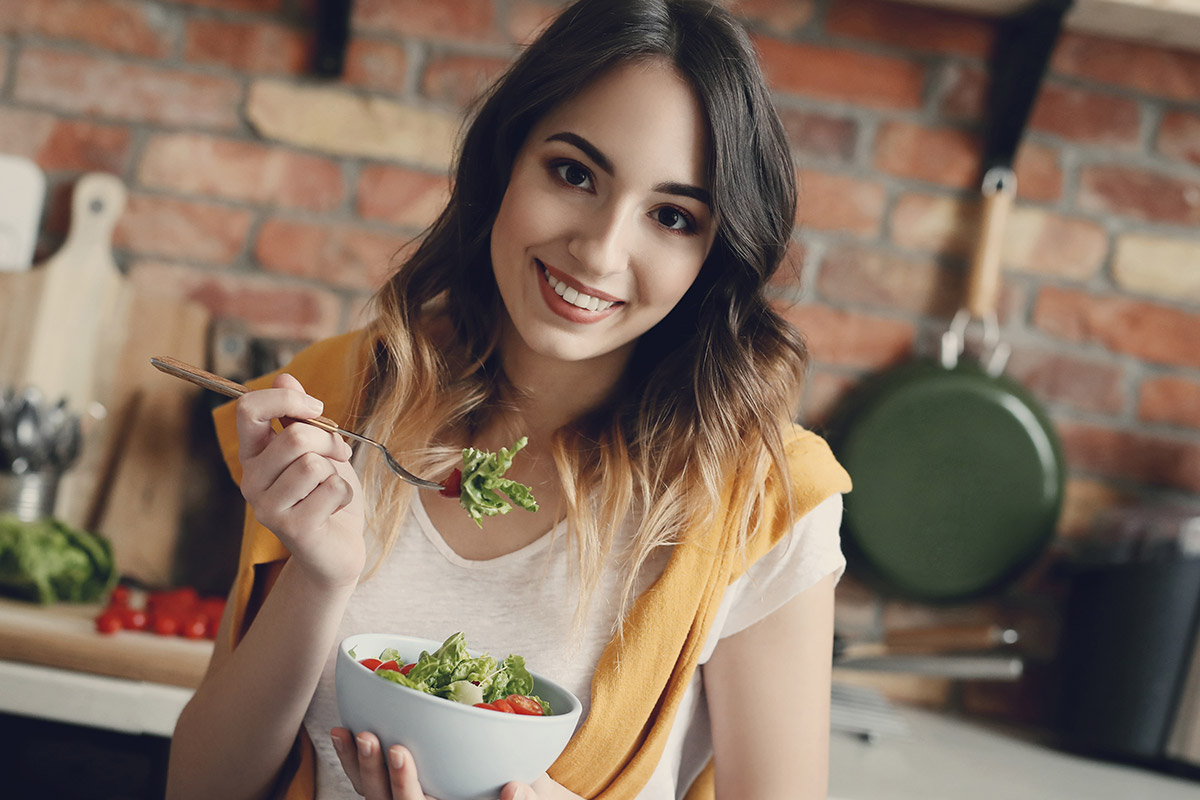

Fueling Your Body for Success: A Nutrition Guide
Introduction
Nutrition plays a crucial role in achieving success, whether it be in academics, sports, or daily life. What you eat directly impacts your energy levels, mental clarity, mood, and overall performance. This comprehensive guide will explore the essential elements of nutrition that can help you fuel your body effectively, leading to success in your endeavors.
1. Understanding the Basics of Nutrition
1.1 Macronutrients: The Building Blocks
To fuel your body efficiently, it’s important to understand the three main macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each of these plays a distinct role in supporting your overall health and performance.
- Carbohydrates: They are the primary source of energy for your body and brain. Complex carbohydrates, like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide sustained energy, while simple carbohydrates, found in sugary foods, can lead to quick energy spikes and crashes.
- Proteins: Essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues, proteins are crucial for muscle development and recovery. Good sources include lean meats, fish, dairy, legumes, and plant-based proteins like quinoa and tofu.
- Fats: While often misunderstood, healthy fats are vital for hormone production, brain health, and nutrient absorption. Incorporate sources of unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, while minimizing saturated and trans fats found in processed foods.
1.2 Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for various bodily functions, from immune support to energy production. Although needed in smaller amounts than macronutrients, their importance cannot be overstated.
- Vitamins: These organic compounds (like vitamin C, D, and B vitamins) support immune function, energy metabolism, and overall well-being. A colorful diet rich in fruits and vegetables helps ensure you get a wide range of vitamins.
- Minerals: Essential minerals (such as calcium, iron, and potassium) contribute to bone health, muscle function, and overall metabolic processes. Include sources like leafy greens, dairy, nuts, seeds, and lean meats to meet your mineral needs.
2. Building a Balanced Plate
2.1 The Plate Method
Creating a balanced meal is crucial for fueling your body effectively. A practical approach is to use the “plate method,” which helps visualize the proportions of different food groups you should include in your meals.
- Half the Plate: Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables (like broccoli, spinach, and carrots) and fruits. These foods are low in calories and high in nutrients.
- One-Quarter of the Plate: Fill one-quarter of your plate with lean proteins (such as chicken, fish, or plant-based proteins) to support muscle health and recovery.
- One-Quarter of the Plate: Fill the final quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables (like quinoa, brown rice, or sweet potatoes) for energy.
2.2 Hydration
Don’t overlook the importance of hydration! Water is essential for optimal bodily function, including digestion, nutrient absorption, and temperature regulation.
- Stay Hydrated: Aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, adjusting based on activity level, climate, and individual needs.
- Hydration Tips: Carry a water bottle with you, drink a glass of water before meals, and incorporate hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges into your diet.
3. Timing Your Nutrition
3.1 Meal Frequency
The timing and frequency of your meals can significantly impact your energy levels and performance.
- Regular Meals: Aim for three balanced meals and 1-2 snacks throughout the day to keep energy levels stable. This helps prevent hunger pangs and maintains focus.
- Pre-Workout Nutrition: Eating a balanced meal or snack 1-2 hours before exercise can enhance performance. Include a mix of carbohydrates and proteins, such as a banana with peanut butter or Greek yogurt with berries.
3.2 Post-Workout Nutrition
After a workout, your body needs to recover and replenish lost nutrients.
- Recovery Meals: Consume a meal or snack rich in protein and carbohydrates within 30-60 minutes post-exercise to support muscle repair and energy restoration. A smoothie with protein powder and fruit or a turkey sandwich on whole-grain bread are excellent options.
4. Special Considerations for Success
4.1 Nutrition for Mental Clarity and Focus
What you eat can significantly affect your cognitive function, mood, and focus.
- Brain-Boosting Foods: Include omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts), antioxidants (found in berries and dark chocolate), and complex carbohydrates (like oats and quinoa) to support brain health.
- Limit Sugary Snacks: Avoid excessive sugar consumption, which can lead to energy crashes and decreased focus. Opt for healthy snacks like nuts, yogurt, or fruit instead.
4.2 Nutrition for Physical Performance
Whether you’re an athlete or someone looking to enhance physical performance, nutrition plays a vital role.
- Fuel for Endurance: Athletes should focus on carbohydrate-rich meals to sustain energy during prolonged activities. Foods like pasta, rice, and fruits are excellent choices.
- Support Recovery: After intense workouts, prioritize protein-rich foods to aid in muscle recovery and repair.
5. Navigating Challenges
5.1 Dealing with Cravings
Cravings can derail your nutritional goals if not managed effectively.
- Mindful Eating: Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger and fullness cues. Before reaching for a snack, ask yourself if you’re truly hungry or just bored.
- Healthy Alternatives: When cravings strike, opt for healthier alternatives. For example, if you crave something sweet, reach for a piece of fruit or a small piece of dark chocolate instead of a candy bar.
5.2 Eating Out and Social Situations
Eating out or attending social events can make it challenging to stick to your nutrition goals.
- Plan Ahead: Before dining out, review the menu online and choose healthier options. Look for dishes with plenty of vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Practice Portion Control: Restaurant portions are often larger than necessary. Consider sharing a dish or asking for a smaller portion to avoid overeating.
6. Making Nutrition a Habit
6.1 Setting Realistic Goals
Making lasting changes to your nutrition requires setting realistic and achievable goals.
- SMART Goals: Use the SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—to create nutrition goals that will guide you toward success.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a food journal or use a nutrition app to track your meals and progress. This can help you stay accountable and identify areas for improvement.
6.2 Developing Healthy Habits
Consistency is key when it comes to nutrition.
- Meal Planning: Take time each week to plan your meals and snacks. This will help you make healthier choices and avoid impulsive eating.
- Batch Cooking: Prepare larger quantities of meals in advance and portion them out for the week. This makes it easier to grab healthy options when you’re busy.
Conclusion
Fueling your body for success involves understanding the importance of nutrition in your overall well-being. By focusing on a balanced diet rich in macronutrients and micronutrients, timing your meals effectively, and navigating challenges with mindful practices, you can enhance your physical and mental performance.
Ultimately, nutrition is a lifelong journey. By setting realistic goals and developing healthy habits, you can create a sustainable lifestyle that supports your path to success in all aspects of life. Remember, the choices you make today will shape your future—fuel your body wisely, and success will follow!